Mysterium — Advanced Setup
20. November 2023 14:27
A day has passed, but Quality status is still red?
If status does not change to green, make sure nothing is interfering with the node's operation. Most often this is a firewall or your antivirus software.
Make sure that permissions for
myst_nodeare created in the firewall. Run the CMD command line and execute thewf.msccommand. Select the "Inbound Connection Rules" item. Findmyst_node_tcpandmyst_node_udpin the list. Make sure they are allowed all connections.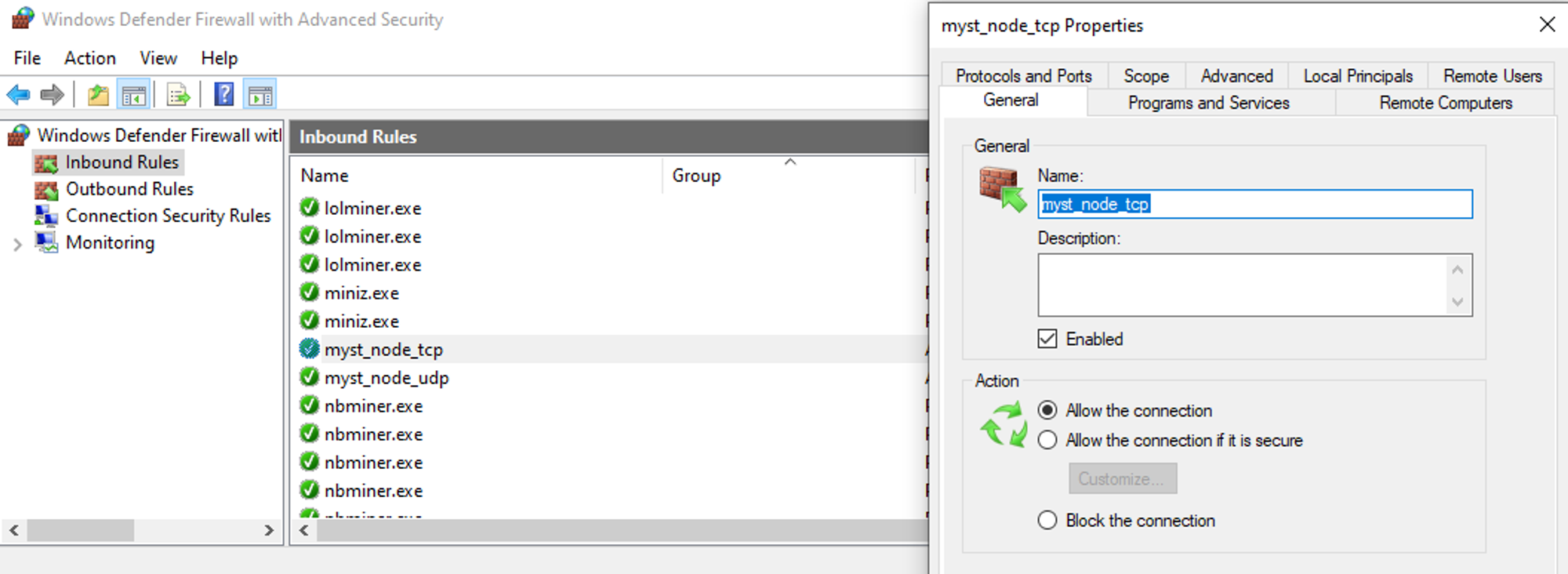
If a third-party antivirus is performing the firewall role on your PC, open its settings and provide such permissions.
- Restart Mysterium. Glitches happen. Restart Mysterium in the Kryptex window.
- Turn off the VPN. If you are using a VPN, you cannot be a node because you are using the services of another node.
- Make sure you haven't launched Kryptex with Mysterium on another PC on the same network. If your PCs are connected to the same network and have the same external IP address, only one PC can work. The other one will most likely fail the check.
- Verify your network connection. If you're using WiFi, consider connecting directly with an Ethernet cable.
- Examine the NAT in the node UI and refer to the Mysterium article on NAT statuses. A stricter and more complex NAT reduces the likelihood of external connections to your node functioning correctly. Mobile Internet typically has the strictest NAT. An ideal scenario involves having a static IP (public/global/external IP) on your router, provided by your Internet Service Provider (ISP).
- Check if your router has a firewall. Disable it or configure it if you're familiar with the process.
- Test your Internet speed. If your speed is below 20 Mbps, Mysterium might consider your connection as "unreliable." In such cases, reach out to Mysterium support to request the removal of restrictions.
- Forward ports on your router. The node generally performs well with Moderate NAT and accepts Most connections (node UI → Settings → Accepting connections). While this setting is optional, it can enhance connection reliability.
- Forward UDP ports used by the node for receiving connections (specified in the node UI → Settings → Advanced → UDP Port range). The current ports for the UDP protocol are in the range 10000:60000.
- In the router settings, this feature might be named “Port forwarding,” “Virtual server,” or something similar, often located near other NAT settings. Typical port forwarding configuration:
- IP address: Specify the local IP address of your computer with the node on the local network.
- Protocol: Specify UDP.
- External port range: Specify 10000:60000.
- Internal port range: If present, also indicate 10000:60000.
- Application name: Set it to “Mysterium” for convenience if the field is available.
- "Allow" checkbox: Enable it if available.
- This setting ensures that the router receives incoming packets on ports 10000:60000 and redirects them to the specific computer on the local network, which is the one with the node.
- If the computer with the node has been offline for an extended period, the router might assign it a different IP address on the local network. However, for port forwarding, it's crucial that this IP address remains unchanged.
- For added reliability, use the Reserved IP setting (usually found near DHCP settings in the router):
- MAC address: The network card of the computer with the node, typically found in the list of connected devices in the router’s web interface or in the network adapter settings in Windows.
- IP address: A fixed local IP address, typically 192.168.x.x, that you always want to assign to this computer.



